Cyberdefenders - EscapeRoom

EscapeRoom
Info
- Category : Digital Forensics
- SHA1SUM : 4dd5e257c4bef0f950a37bb1e401f3dd990929bf
- Published : Aug. 18, 2020, midnight
- Author : The HoneyNet Project
- Size : 15 MB
- Tags : PCAP Wireshark Linux Network
Unzip the challenge (pass: cyberdefenders.org) and use your analysis tools to examine provided PCAPs and log files.
Scenario
You as a soc analyst belong to a company specializing in hosting web applications through KVM-based Virtual Machines. Over the weekend, one VM went down, and the site administrators fear this might be the result of malicious activity. They extracted a few logs from the environment in hopes that you might be able to determine what happened.
This challenge is a combination of several entry to intermediate-level tasks of increasing difficulty focusing on authentication, information hiding, and cryptography. Participants will benefit from entry-level knowledge in these fields, as well as knowledge of general Linux operations, kernel modules, a scripting language, and reverse engineering. Not everything may be as it seems. Innocuous files may turn out to be malicious so take precautions when dealing with any files from this challenge.
Helpful Tools
- Wireshark
- NetworkMiner
- BrimSecurity
- UPX
- IDA
Questions
Q1 - What service did the attacker use to gain access to the system?
It’s not easy to differentiate successful versus failed login attempts in Wireshark. However, some features of the traffic can help to reveal whether or not an attempted authentication is successful :
- Flow length: A successful authentication attempt will result in a longer session than a failed
- Packet size: SSH servers have set responses for successful and failed authentications. Observing the length of the SSH packets can show whether authentication succeeded or failed.
- Packet timing: Packets that require user interaction will take longer than automated ones, making them easier to detect
Statistics > Conversations > TCP tab
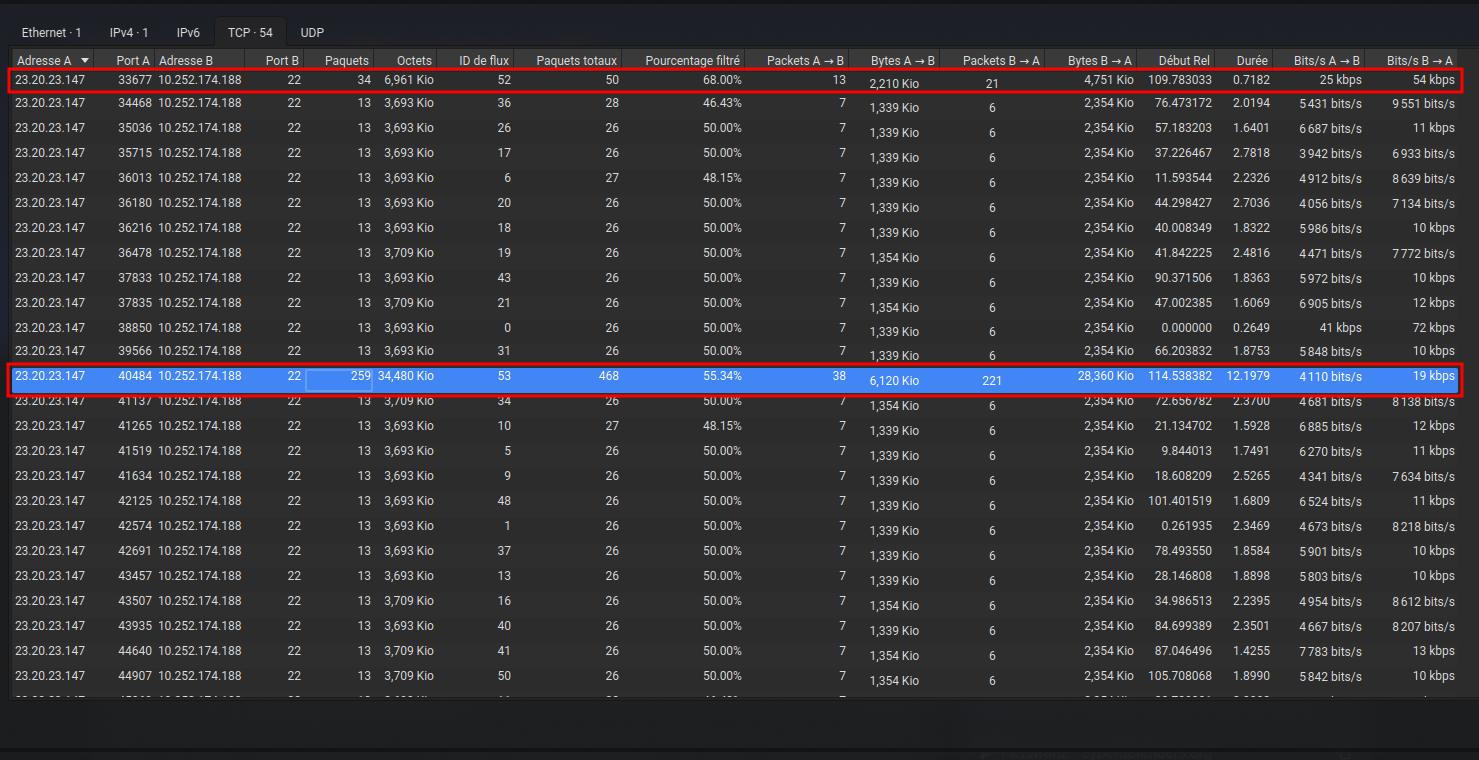
Answer : ssh
Q2 - What attack type was used to gain access to the system?(one word)
With statistics we can see lot of failed. We can deduce ssh-bruteforce attack.
Answer : bruteforce
Q3 - What was the tool the attacker possibly used to perform this attack?
Answer : hydra
Q4 - How many failed attempts were there?
With statistics we can see 54 TCP conversation (all on the port 22) minus 2 success attempts = 52 failed attempts.
Answer : 52
Q5 - What credentials (username:password) were used to gain access? Refer to shadow.log and sudoers.log.
In shadow.log, we get hashed password.
|
|
Answer : manager:forgot
Q6 - What other credentials (username:password) could have been used to gain access also have SUDO privileges? Refer to shadow.log and sudoers.log.
Refer to the previous question.
|
|
Answer : sean:spectre
Q7 - What is the tool used to download malicious files on the system?
In the PCAP, after all ssh request we can see TCP request on port 80 (we can guess HTTP traffic). Follow TCP stream
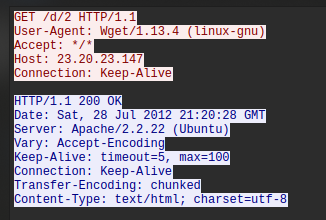
Answer : wget
Q8 - How many files the attacker download to perform malware installation?
Export Objects > HTTP
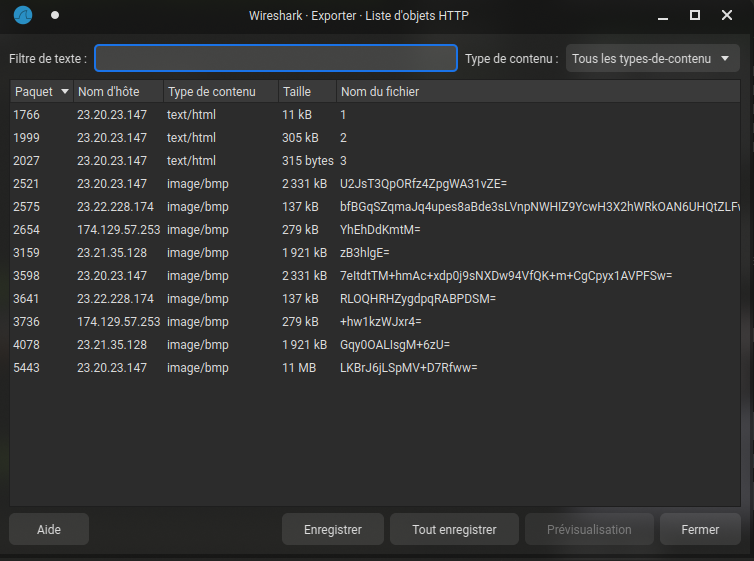
Answer : 3
Q9 - What is the main malware MD5 hash?
|
|
|
|
|
|
Answer : 772b620736b760c1d736b1e6ba2f885b
Q10 - What file has the script modified so the malware will start upon reboot?
In Linux, the /etc/rc.local file is a system initialization script that is executed during the boot process. It is typically used to run custom commands or scripts that need to be executed automatically at system startup.
The nohup command stands for “no hangup.” It is used to run a command or script in the background, even if the user logs out or terminates their session. When you run a command with nohup, it prevents the command from being terminated when the terminal session ends. Any output generated by the command is redirected to a file called “nohup.out” by default.
Answer : /etc/rc.local
Q11 - Where did the malware keep local files?
According to the bash script file.
Answer : /var/mail/
Q12 - What is missing from ps.log?
The 1-ELF file renamed and move to /var/mail/mail must be launch.
Answer : /var/mail/mail
Q13 - What is the main file that used to remove this information from ps.log?
In Linux, the /etc/modules file is a configuration file that lists kernel modules to be loaded at system startup. According to the bash script file. we can see that the file 2-ELF is stored in the “/etc/modules” folder as sysmod.ko
In resume, 1-ELF and 3-scripts so we can deduce that 2-ELF is used to clean informations about 1-ELF.
Answer : sysmod.ko
Q14 - Inside the Main function, what is the function that causes requests to those servers?
We need to focus on 1-ELF.
|
|
We got an interesting information : This file is packed with the UPX executable packer http://upx.sf.net
UPX Unpacker to unpack files compressed with UPX by Oberhumer, Molnár & Reiser (see upx.github.io).
|
|
Get more informations :
|
|
Decompress :
|
|
Strings + grep :
|
|
Answer : requestFile
Q15 - One of the IP’s the malware contacted starts with 17. Provide the full IP.
I make a regex to find IP :
|
|
Answer : 174.129.57.253
Q16 - How many files the malware requested from external servers?
IPs match with BMP files whose are download.

Answer : 9
Q17 - What are the commands that the malware was receiving from attacker servers? Format: comma-separated in alphabetical order
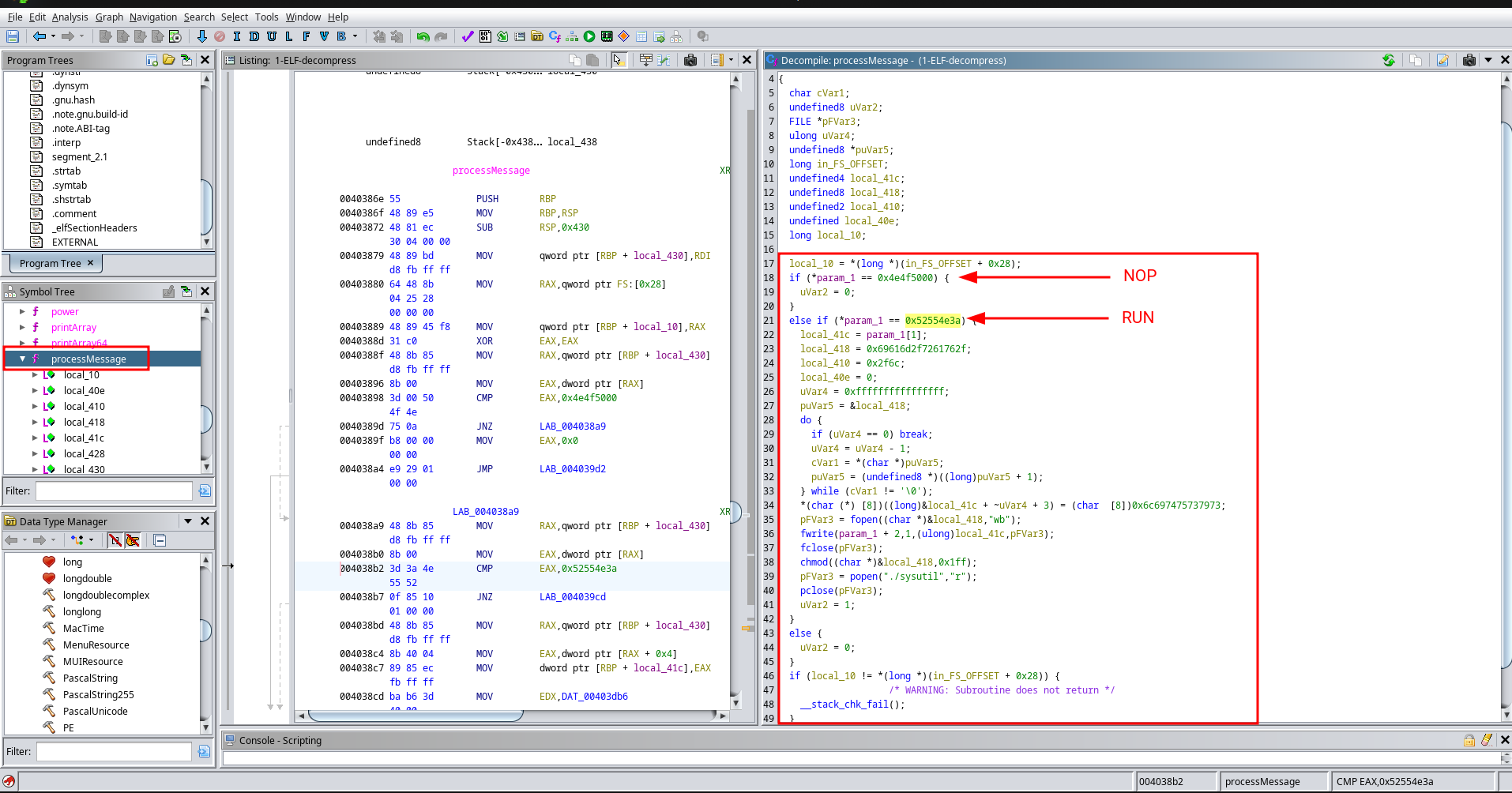
|
|
Answer : NOP,RUN