FCSC 2023 - APT Style

APT Style
Catégorie : forensics
Description générale pour la série
En tant que RSSI, vous anticipez ~ tardivement ~ la migration des postes utilisateur de votre parc vers Windows 10.
Pour ce faire, vous demandez à l’un de vos collaborateurs de préparer un ISO d’installation et, devant l’importance de l’innocuité de ce média d’installation, vous décidez de le tester. Vous observez d’étranges comportements sur la machine fraîchement installée… Vous décidez alors de décortiquer cet ISO, afin de comprendre d’où viennent ces comportements.
Attention : pour ces épreuves, vous n’avez que 10 tentatives de flag par épreuve.
Toutes les épreuves de cette série utilisent le même fichier disponible ci-dessous.
SHA256(Win10_22H2_French_x64.iso) = 6b308977cecc9b6d8aa50a8ddabdacdf01394b0819d5978141ed61862c61143f
APT Style 1/7
Difficulté : ⭐ ⭐ ⭐
Énoncé
Quel objet déclenche le comportement malveillant ? La réponse attendue est le chemin de l’objet.
Quel groupe d’attaquants emploie une méthode similaire ? Le format attendu est UNCXXXX.
Le flag final est au format FCSC{chemin:UNCXXXX}
Solve
|
|
|
|
J’ai récupérer une ISO officiel de Windows afin de la comparer avec le fichier donné :
|
|
On va regarder les fichiers différents :
|
|
“install.wim” est un fichier utilisé par le système d’exploitation Microsoft Windows pour stocker une image complète du système d’exploitation, y compris tous les fichiers et paramètres nécessaires à l’installation de Windows.
Pour extraire les fichier de install.wim, on va devoir installer wimlib :
Dans un premier temps, on va déterminer quelle image extraire des 2 ISO.
|
|
L’ISO donnée contient une unique image Win10 Pro, l’ISO que j’ai téléchargé en contient 11. On va extraire le install.wim de la 6ème :
|
|
|
|
On va refaire un diff sur les nouveaux fichiers :
|
|
On découvre que c’est potentiellement une clé de registre qui a été modifié, on va donc l’extraire et analyser les clés.
Pour cela, je vais passer sur une machine Windows et utiliser : RegistryChangesView
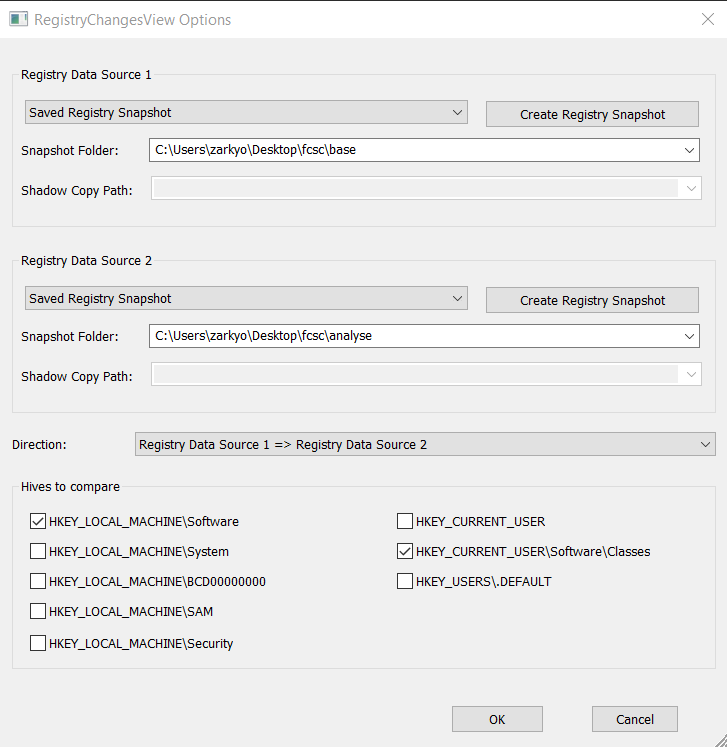
On voit bien les clés qui ont été modifiées, ajoutées ou supprimées :
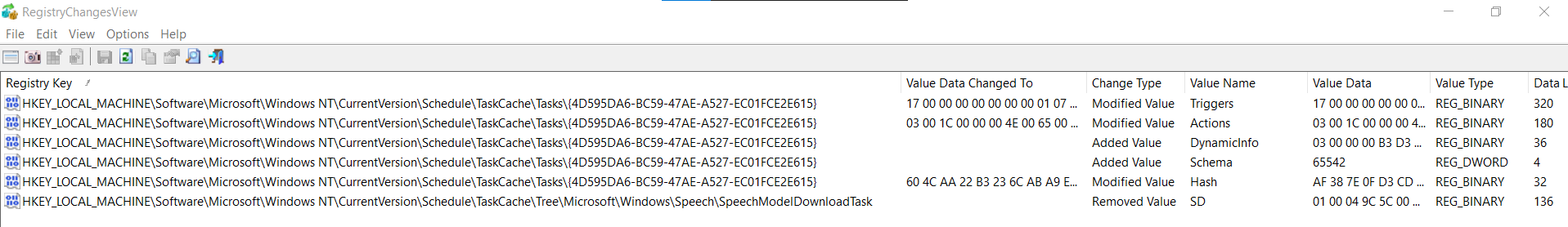
On ouvre dans registry explorer la ruche pour aller regarder les valeurs de ces clés et on remarque une clé avec une commande powershell :
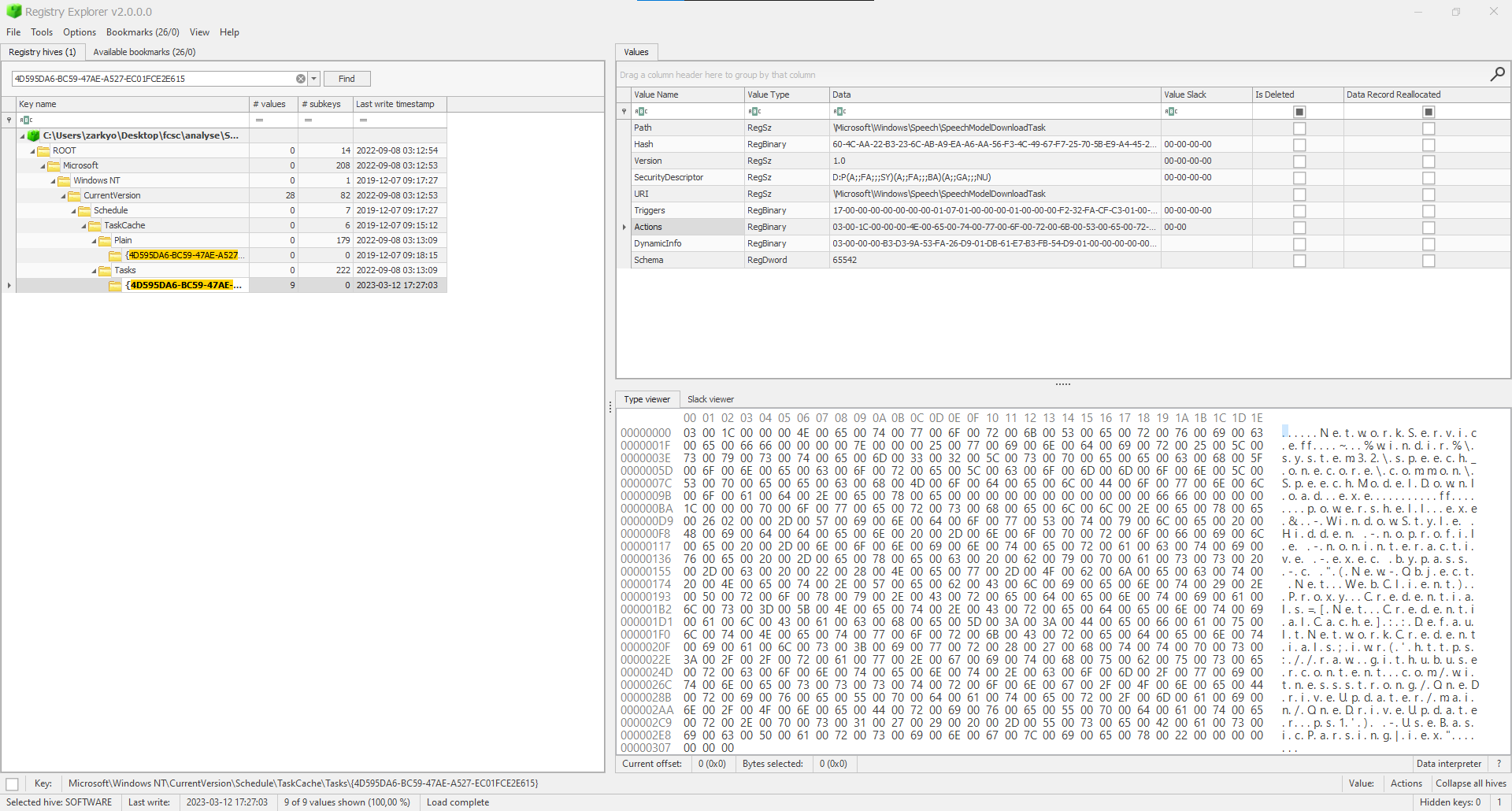
|
|
Sur le github, on peut avoir le code de OneDriveUpdater.ps1. On a également d’autre fichiers (script, dll, exe) dans le dépôt : https://github.com/witnessstrong/OneDriveUpdater
OneDriveUpdater.ps1:
|
|
On arrive plus ou moins à comprendre le powershell sans trop le remettre en forme.
En ce qui concerne l’UNC, une petite recherche google sur les compromissions d’ISO et on arrive sur cette page : https://www.mandiant.com/resources/blog/trojanized-windows-installers-ukrainian-government
Flag : FCSC{HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Schedule\TaskCache\Tasks{4D595DA6-BC59-47AE-A527-EC01FCE2E615}:UNC4166}
APT Style 2/7
Difficulté : ⭐ ⭐ ⭐
Énoncé
Quel élément a été supprimé afin de masquer ce comportement malveillant à Windows ? La réponse attendue est le chemin de l’élément supprimé.
Quel groupe d’attaquant emploie une méthode similaire ? La réponse attendue est le nom du groupe.
Le flag est au format FCSC{chemin:nom du groupe}.
Solve
La seule valeur de clé qui est supprimé est la SD (Security Descriptor).
On va sur le site du Mitre pour voir les techniques sur la modification de clé de registre : https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1112/
Un coup de CTRL + f --> SD
|
|
On remonte au groupe HAFNIUM
Flag : FCSC{HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Schedule\TaskCache\Tree\Microsoft\Windows\Speech\SpeechModelDownloadTask\SD:HAFNIUM}
APT Style 3/7
Difficulté : ⭐
Énoncé
Quel fichier est utilisé comme base de timestomp des fichiers malveillants ? La réponse attendue est le chemin complet du fichier au format : FCSC{chemin}.
Solve
Dans le powershell, on peut voir un bout de code qui réalise le changement de timestomp :
|
|
Il suffit de comprendre à quoi correspond la valeur de $ts. Celle-ci est égale C:\Windows\win.ini.
Flag : FCSC{C:\Windows\win.ini}
APT Style 4/7
Difficulté : ⭐
Énoncé
Quelle technique est employée par l’attaquant pour exécuter la charge malveillante ? La réponse attendue est l’ID complet de la technique au sens de la matrice MITRE ATT&CK, au format FCSC{TXXXX.XXX}.
Solve
On a le dépôt github avec des scirpts powershell, un exe et notamment 2 DLLs avec plus ou moins le même nom.
Sur le site du Mitre, on peut trouver cette technique Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side-Loading ; https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1574/002/
Flag : FCSC{T1574.002}
APT Style 5/7
Difficulté : ⭐
Énoncé
Note : il semblerait que l’attaquant ait supprimé de son répertoire en ligne la DLL malveillante… L’administrateur ayant observé les comportements malveillants a fait l’installation le 15/03/2023
Quel est le numéro de série du certificat ayant servi à signer la DLL malveillante ? La réponse attentue est au format FCSC{numéro de série}.
Solve
On cherche le numéro de série du certificat ayant servi à signer la DLL malveillante. On peut avoir cette information en allant dans les propriétés de la DLL.
On clone : https://github.com/witnessstrong/OneDriveUpdater
La DLL version.dll n’est pas une DLL. On fait donc un sigcheck sur verslon.dll pour avoir le “Serial Number”. On essaye le flag et ca ne fonctionne pas.
On reprend l’énnoncé et on regarde la note :
Note : il semblerait que l’attaquant ait supprimé de son répertoire en ligne la DLL malveillante… L’administrateur ayant observé les comportements malveillants a fait l’installation le 15/03/2023
Si on veut récupérer un ancien fichier, il faut utiliser WayBackMachine.
On retrouve notre dépôt le 15/03/2023 : https://web.archive.org/web/20230315194209/https://github.com/witnessstrong/OneDriveUpdater
Si on veut récupérer les fichiers, il faut cibler un ancien commit : https://web.archive.org/web/20230315194218/https://github.com/witnessstrong/OneDriveUpdater/commit/575769e48d086b0e5468577a011c2322690d471a
ON télécharge les DLLs :
- version.dll : https://raw.githubusercontent.com/witnessstrong/OneDriveUpdater/575769e48d086b0e5468577a011c2322690d471a/version.dll
- verslon.dll : https://raw.githubusercontent.com/witnessstrong/OneDriveUpdater/575769e48d086b0e5468577a011c2322690d471a/verslon.dll
On récupère les “Serial Number” :
|
|
|
|
La DLL malveillant est version.dll, elle avait bien été supprimer et remplacer par un autre fichier.
Flag : FCSC{43bb437d609866286dd839e1d00309f5}
APT Style 6/7
Difficulté : ⭐
Énoncé
Note : il semblerait que l’attaquant ait supprimé de son répertoire en ligne la DLL malveillante … L’administrateur ayant observé les comportements malveillants a fait l’installation le 15/03/2023
Quelle machine est ciblée par la charge malveillante ? La réponse attendue est le nom de la machine au format FCSC{nom}.
Solve
Un string suffit a obtenir le nom de la machine ciblée :
|
|
Flag : FCSC{DESKTOP-3BY599R}
APT Style 7/7
Difficulté : ⭐ ⭐
Énoncé
Note : il semblerait que l’attaquant ait supprimé de son répertoire en ligne la DLL malveillante … L’administrateur ayant observé les comportements malveillants a fait l’installation le 15/03/2023
Quel C2 est contacté par la charge malveillante ? Le flag est au format FCSC{IP:PORT}.
Solve
Pour récupérer les informations du C2, on va réaliser une analyse dynamique en exécutant le OneDriveStandaloneUpdater.exe et analyse capturer/analyser le traffic réseau avec Wireshark
Attention : il est nécéssaire de mettre le bon hostname à la VM pour que le payload se déclenche

On remarque directement le port 1337, référence au leet speak, de l’anglais « elite speak »
Flag : FCSC{192.168.56.1:1337}